What Are the Major Differences in the Two Reaction Pathways
The dorsal columnmedial lemniscus pathway is an important sensory neural pathway of the nervous system. Both of these reactions involve many steps.
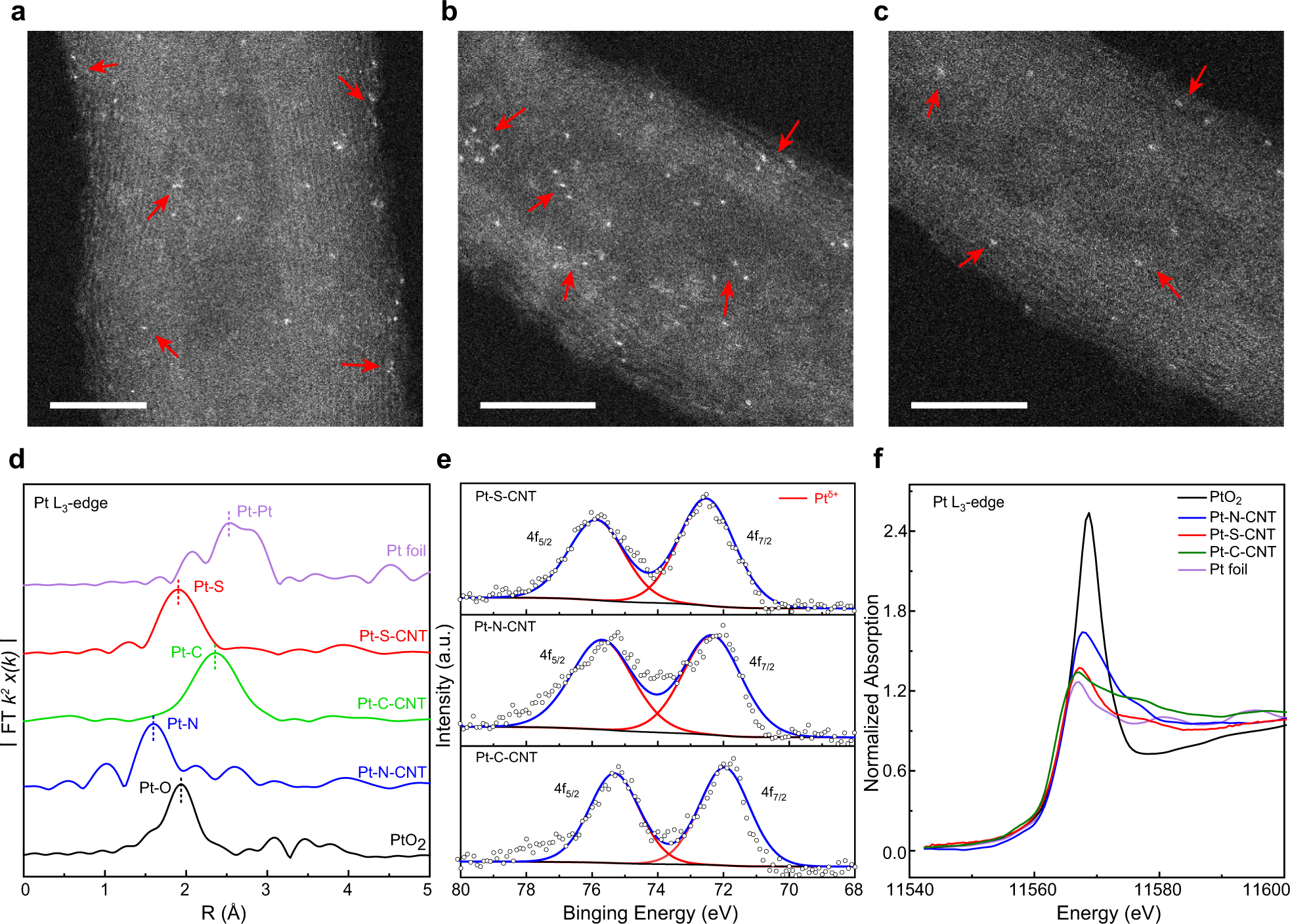
Manipulating The Oxygen Reduction Reaction Pathway On Pt Coordinated Motifs Nature Communications
The two opposing pathways may share one or more reversible reactions however there will always be at least one enzymatic step that is different.

. The processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two examples of metabolic pathways. The change in energy with an extra notion on the transition states. Is each of the following statements true or false.
During the light reaction stage the green part of the plant traps energy from the sunlight and synthesize energy-rich chemical molecules. B For both paths the rate of the reverse reaction is slower than the rate of the forward reaction. What is the main difference between these two methods.
Complete the following reaction pathways by filling in any missing reagents intermediate compounds or products. Further difference between ED pathway and PP pathway is the generation of reduced NADPH from NADP in the former. The major difference involved between these two types of reactions is to study the different properties of the departure group that helps us in finding out the pathway of the group.
The primary chemical reaction pathway is the conversion of sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide which is coupled with biomass growth and heat generation from the exothermic reaction. Cellular respiration is an important catabolic pathway necessary for the creation of ATP molecules. In addition SN1 pathway is a multi-step.
3 with an emphasis on two modifications. In grief self-esteem is usually not affected. Anabolic pathways synthesize molecules and require energy.
The lesson provides detailed insight into the difference between C3 C4 and CAM pathways for easier. The major steps of the reaction pathway for EC phenol degradation are summarized in Fig. In depression the focus is on self.
Two major classes of metabolic reactions Catabolic pathways Break larger molecules into smaller products Exergonic release energy Anabolic pathways Synthesize large molecules from the smaller products of catabolism Endergonic require more energy than they release. In depression loathsome feelings toward oneself. The first-order neurons have their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia each with one process that contributes to a peripheral nerve and another that enters the spinal cord.
But S N 1 represents unimolecular reactions where the reaction rate can be expressed by rate K R-LG. It helps a person to locate the difference between two points. Students also viewed these Chemical Engineering questions.
Another main difference between the two is that grief is associated with a specific event or loss of a loved one but with depression there isnt always an identifiable loss. C3 cycle occurs in all plants at 20-25 degrees Celsius whereas the C4 cycle occurs only in C4 plants at 30-45 degrees Celsius. Afterwards Pyruvate can be completely oxidized to CO 2 and H 2 O by enzymes present in the mitochondria.
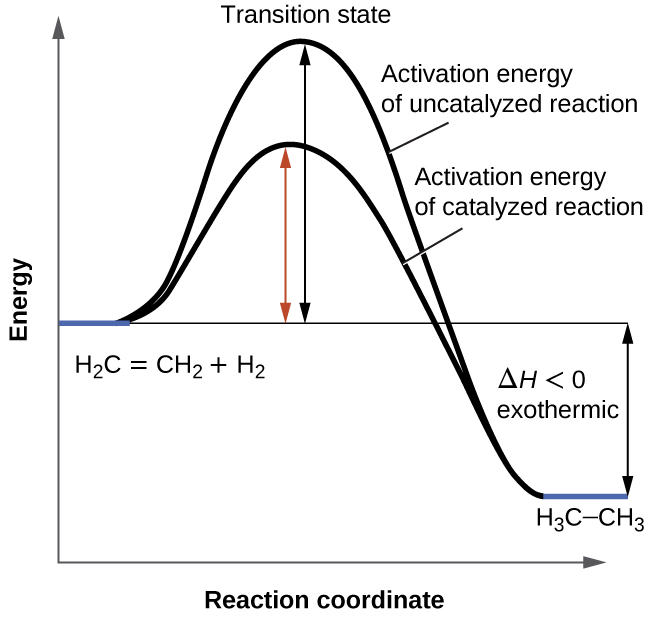
Because almost all metabolic reactions take place non-spontaneously proteins called enzymes help facilitate those chemical reactions. Concurrently a range of species are formed at low concentrations by a multitude of side reactions many of which impact product flavour considerably. The following graph shows two different reaction pathways for the same overall reaction at the same temperature.
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and completes in a series of ten reactions. This seems that EMP pathway more efficient than that of ED pathway. Usually with the reaction mechanism the sequence of events electron transfers is indicated while the term reaction pathway usually refers to the reaction coordinate diagram associated with the reaction ie.
C3 and C4 cycle are the two types of dark reactions that occur during photosynthesis. Unlike S N 1 S N 2 represents bimolecular reactions and the rate of reaction can be expressed by rate K R-LG Nu. Hint 1 2 4 5 - We have two methods for converting alcohols into alkyl halides.
A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it step-by-step through a series of metabolic intermediates eventually yielding a final product. Both types of pathways are important parts of an organisms metabolism. S N 1 and S N 2 are two different types of nucleophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry.
Another name for this pathway is the PCML pathway. The differences between the photofragmentation pathways are related to the. The differences in these pathways creates flexibility.
Glycolysis is the major pathway for glucose metabolism in which glucose will convert to pyruvate under aerobic condition or lactate anaerobic. On the other hand the dark reaction stage is where plants use energy-rich molecules to synthesize carbohydrates and carbon dioxide. The main difference between the two pathways is the location of the second neuron which in turn determines where each pathway crosses the midline.
The catabolism of glucose results in production of only one ATP molecule whereas in EMP pathway two ATP molecules are produced. The following graph shows two different reaction pathways for the same overall reaction at the same temperature. If a biosynthetic pathway is blocked the body is sometimes able to use the reverse of the catabolic pathway to make the same compound.
B How can there be two different reaction pathways for the same reaction at the same temperature. Hence the EC phenol degradation pathway theory needs to be modified to reconcile it with the experimental observations although the main routes of the pathway can still be followed. Catabolic pathways break down molecules to release energy while anabolic pathways use energy to create new molecules.
For a full list of differences between the two check out the tabular column. In grief the focus is on the loss. The major difference between photolysis at 260 and 390 nm is that in the first case Ru3CO10mu-CO is formed by bimolecular recombination of Ru3CO10 with a free CO in 50 ns whereas in the second case it forms directly from Ru3CO12 at the onset of the reaction.
During C3 cycle a single carbon fixation event is observed whereas during C4 cycle two carbon fixation events are observed. A Which pathway is slower. Catabolic pathways break down molecules and produce energy.
Understanding the major differences between these two will give us the key differences between one and the other. A The rate is faster for the red path than for the blue path.

Photosystem I And Photosystem Ii Teaching Biology Systems Biology Photosynthesis
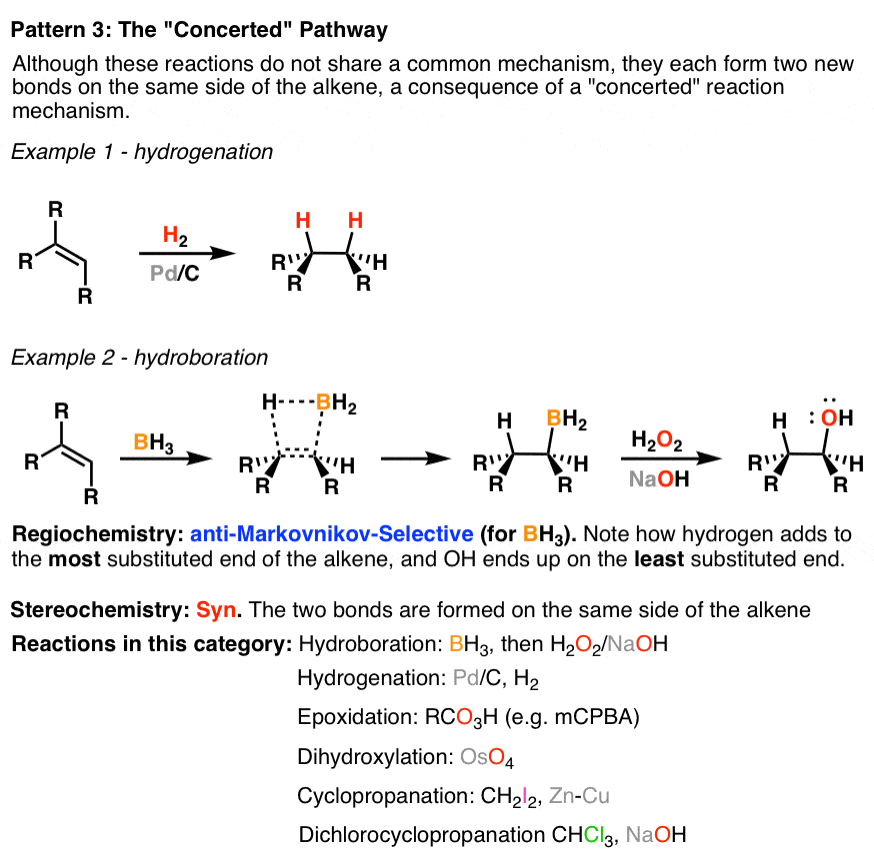
Summary Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms
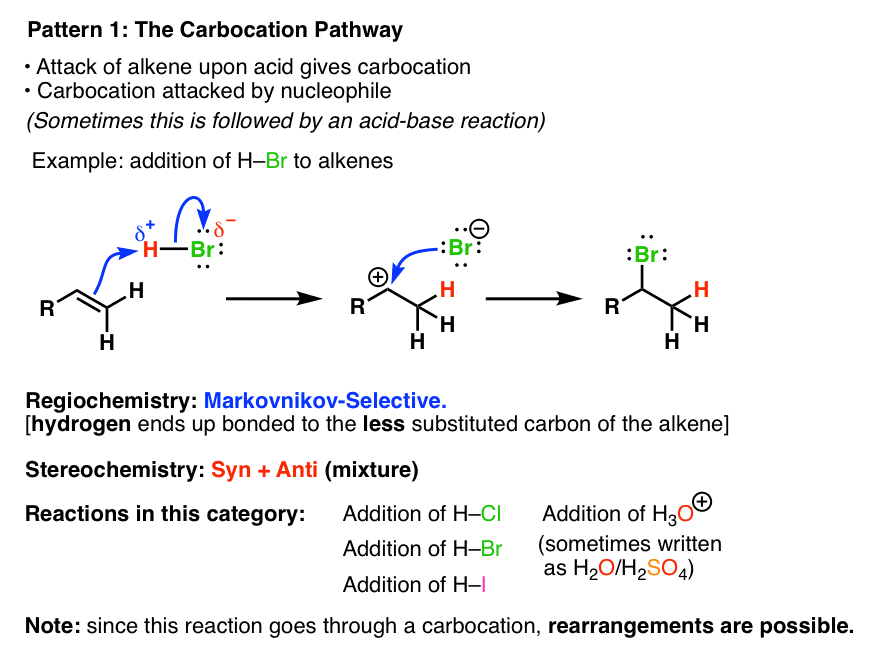
Summary Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms

Cell Metabolism Learn Science At Scitable

Comparing The E1 And E2 Reactions Master Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Worksheets

Alkyl Halides And Elimination Reactions Organic Reactions Reactions Functional Group

C3 C4 And Cam Plants Biology Diagrams Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Biology Plants

Difference Between Cyclic And Noncyclic Photophosphorylation Comparison Summary Human Digestive System Digestive System Diagram Digestive System

Glycolysis Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Organic Chemistry Books

Pin On Akonneh2020 Sainteugeneschool Org
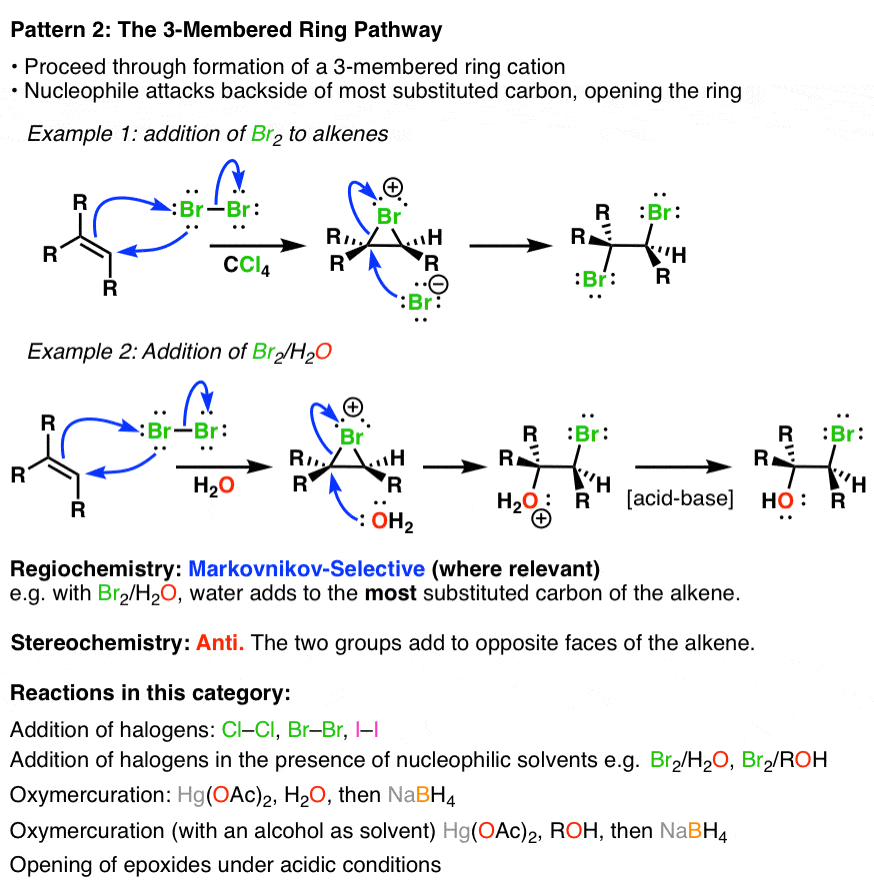
Summary Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms

Learn All About Photosynthesis With This Study Guide Photosynthesis Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration

Difference Between Sn1 And Sn2 Reactions Infographic Study Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Organic Chemistry




Comments
Post a Comment